Highlighted Articles
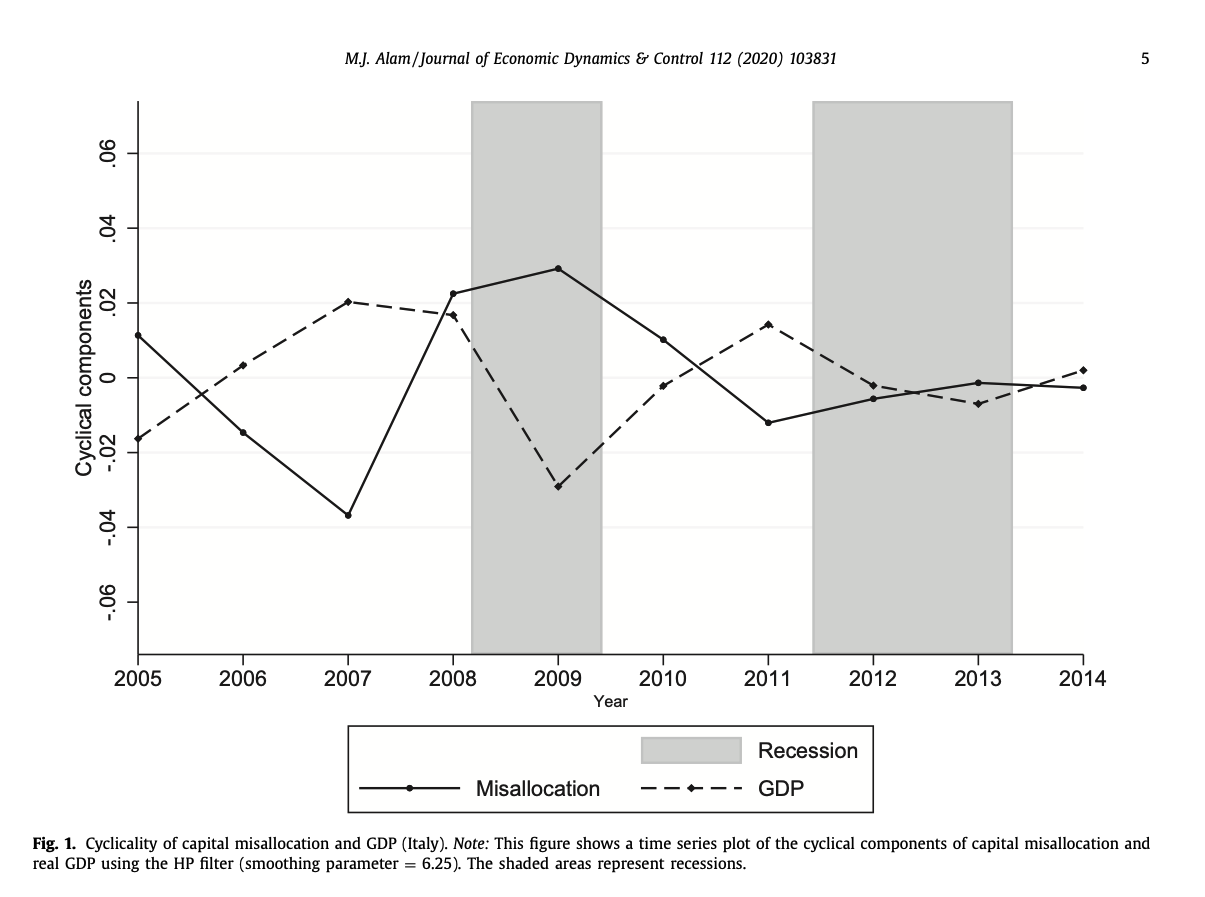
Capital Misallocation: Cyclicality and Sources
Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control
March 2020
Abstract: Capital misallocation can lower aggregate total factor productivity, but much less is known about its cyclicality. Using European firm-level data for 2005 to 2014, I establish that capital misallocation, as measured by the dispersion of returns to capital, is higher during recessions and lower during booms. This result is robust to using a much longer dataset from Compustat for the United States and Canada. I also find that firms’ net worth, measured as the difference between total assets and liabilities, relative to sales, can explain more capital misallocation than all the other examined firm-level factors combined. Furthermore, my results suggest that firms’ net worth explains approximately 10 percent of capital misallocation and 30 percent of its cyclicality.
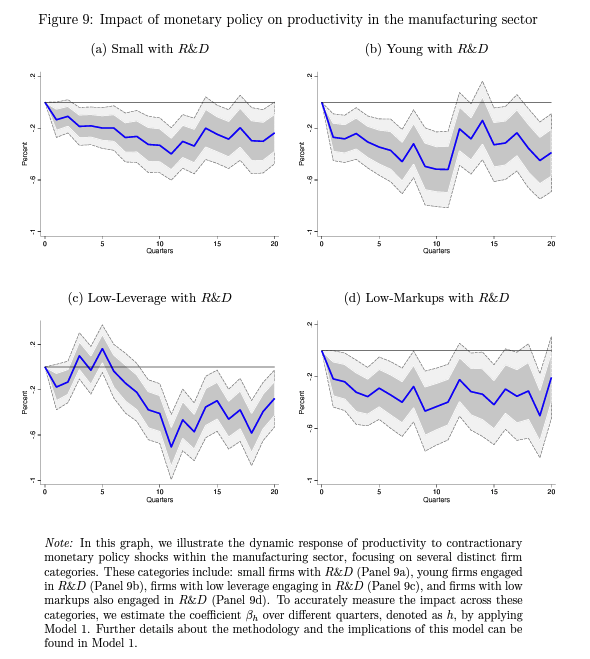
The Long-Run Effects of Monetary Policy: The Role of R&D Investment in Economic Growth
with Eskander Alvi
Economic Modeling
August 2024
Abstract: This study examines the long-term economic effects of monetary policy, focusing on its impact on research and development (R&D) investment and firm productivity. Using data from Compustat, we analyze the response of productivity to monetary policy shocks, with an emphasis on the role of firm size, age, and leverage as indicators of credit constraints. We use high-frequency financial market data for identifying monetary policy shocks through a Local Projections-Instrumental Variables (LP-IV) approach. Our findings reveal that smaller, younger, and less leveraged firms are more adversely affected by contractionary monetary policies, suggesting a significant impact on their R&D investments and subsequent productivity, particularly in the manufacturing sector. The findings also highlight that tight monetary policy has a persistent negative impact on firm productivity via reduced R&D investment, underscoring the need for policies like R&D subsidies to support long-term economic growth.
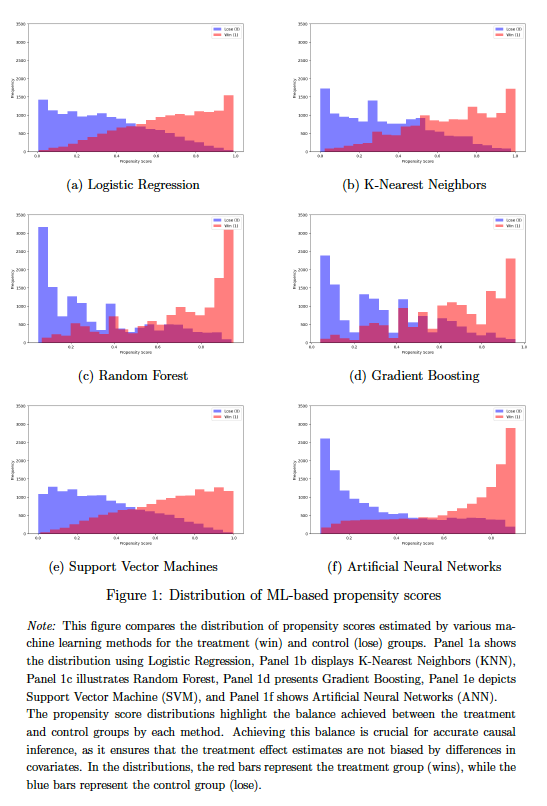
Applying Machine Learning Methods in Causal Estimation: Analyzing the Benefits of College Athletic Success
with Gerard Tetegan
Journal of Comments and Replications in Economics (Under review)
July 2024
Abstract: This study investigates the causal effect of college athletic success on institutional benefits, employing the dataset from Anderson (2017). We contribute to the literature by implementing machine learning algorithms for propensity score estimation, effectively capturing non-linear relationships without explicit specification. Our results demonstrate that machine learning models, particularly neural networks and gradient boosting, significantly outperform traditional logistic regression in handling non-linearities and reducing bias. Gradient boosting, in particular, provides the most robust estimates, enhancing the precision and reliability of causal inferences. The analysis reveals that athletic success decreases acceptance rates while boosting donations, applications, academic reputation, in-state enrollment, and incoming SAT scores. This research underscores the efficacy of machine learning in improving causal inference in observational studies, highlighting its potential for broader application in policy and institutional decision-making.
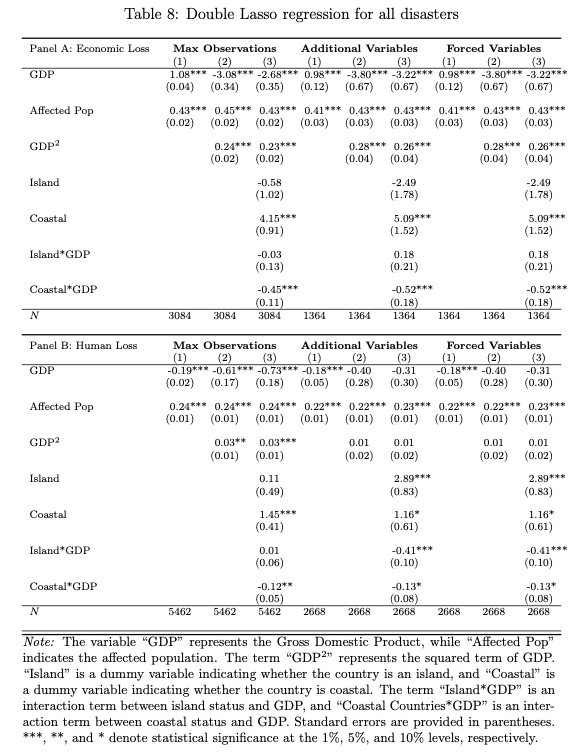
Identifying Macro Determinants of Natural Disaster: Applying Machine Learning Approach
with Pallab Mozumder
Computational Economics (Submitted)
October 2024
Abstract: This study analyzes the macroeconomic determinants of human and economic losses caused by natural disasters using machine learning techniques, particularly the double lasso regression framework. By focusing on floods, storms, and earthquakes, we examine the complex relationships between economic development, geographical characteristics, and the severity of disaster impacts. Our findings indicate a U-shaped relationship between GDP per capita and economic losses, where initial GDP growth reduces losses until a threshold is reached, beyond which further economic development increases the financial damages. Human losses, on the other hand, show an inverse U-shaped relationship with GDP in the case of floods, highlighting that while higher GDP initially leads to more fatalities, continued economic growth eventually reduces mortality rates. Moreover, we find that coastal countries are more vulnerable to both human and economic losses compared to island and landlocked countries, though they demonstrate a greater capacity to leverage GDP growth in reducing economic losses. These results underscore the importance of tailored disaster risk management strategies that consider both economic development and geographic factors to mitigate the adverse impacts of natural disasters.
The Convenience Yield Channel of Monetary Policy and International Stock Prices
with Matthew Schaffer and Rashed Sardar
Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions & Money (R&R)
March 2024
Abstract: Krishnamurthy and Lustig (2019) propose a convenience yield channel of monetary policy, whereby Federal Reserve decisions affect global financial variables via their influence on the convenience yield of dollar-denominated safe assets. We document that the convenience yield channel contributes to the spillover of Fed policy to international stock markets. Following a surprise monetary tightening, the convenience yield differential between US Treasuries and equivalent foreign government bonds grows. A monetary policy-induced increase in the convenience yield differential, in turn, results in a decline in international stock indexes. This decline cannot be explained by movements in interest rates or exchange rates but instead seems likely to be driven by a higher equity risk premium. While policy-induced changes in convenience yield differentials contribute to international spillovers of Fed policy, a wider differential (in levels) can help to insulate foreign markets from the cumulative impact of Fed policy decisions.
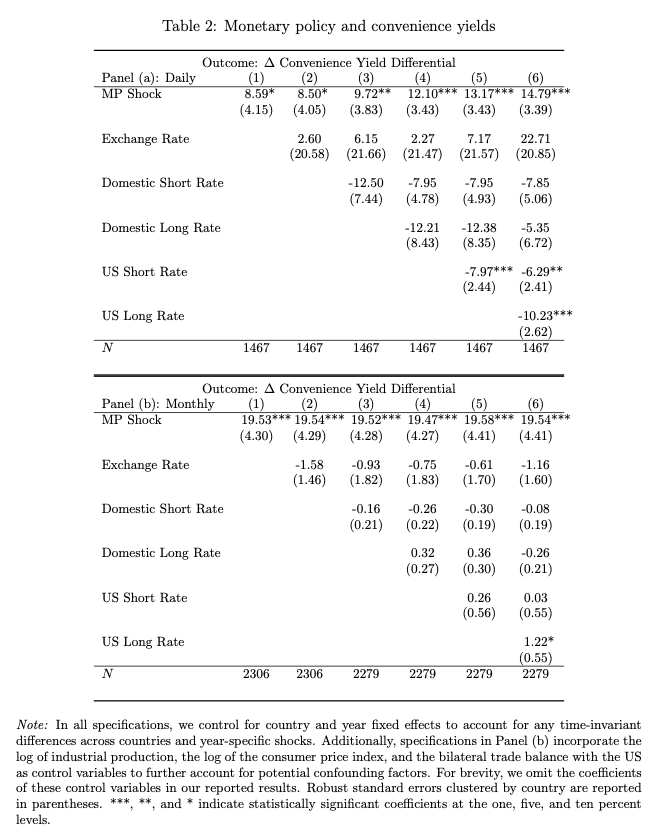
Price Dispersion and Trade Policy
Review of International Economics (R&R)
June 2024
Abstract: This study examines the impact of the Canada-United States Free Trade Agreement (FTA) on producer prices at the product level in Canada. The effect of trade reforms on producer price dispersion is not straightforward: while increased competition may compress the price distribution among producers, access to new niche markets and product differentiation may lead to more dispersed prices. The study uses newly compiled Canadian product-level data and observes a significant increase in product price dispersion in Canada due to the FTA. To establish a causal relationship, the study employs a difference-indifferences (DiD) approach, treating the FTA as a quasiexperiment. The results show that export-oriented products contributed the most to Canada's price dispersion rise. The study also found that trade exposure decreased the number of products produced by a plant and increased the likelihood of discontinuing a high-priced product.
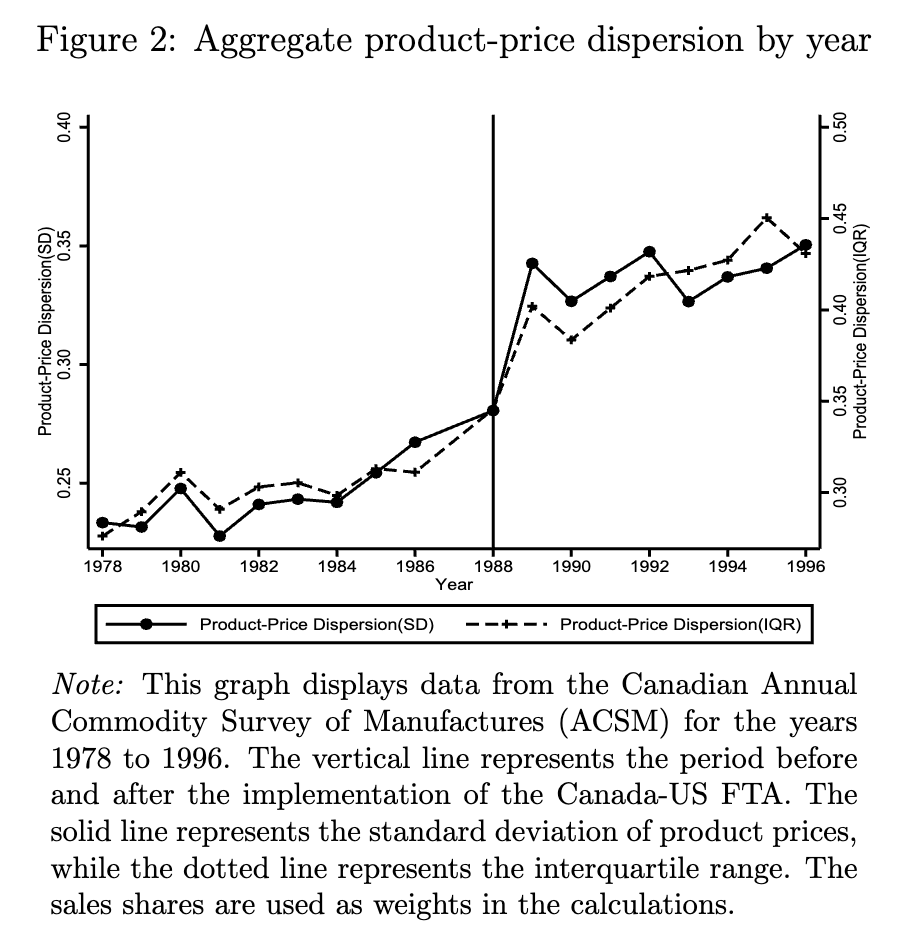
Spatial Misallocation in Canada
with Herb Emery
Canadian Journal of Regional Science (Forthcoming)
October 2024
Abstract: Factor misallocation across firms has been well-documented and for Canada, it appears that spatial misallocation of labour and capital across regions may have important implications for national economic growth. Spatial misallocation hinders economic efficiency by preventing resources from being allocated to their most productive uses, thereby constraining growth. Using Canadian data from 2000 to 2018, we find that labour productivity increased by approximately 1% annually, while capital productivity declined by around 1% per year coincident with an increase in the spatial misallocation of labour increased and a decrease in the spatial misallocation of capital. We examine the factors correlated with these inefficiencies and find that production subsidies are positively associated with higher spatial misallocation of factors, suggesting that such subsidies may help sustain less productive firms, dampening national economic growth.
Federal Statistical Research Data Center Projects on Monetary Policy
Project with Pedro Bento and Tatevik Sekhposyan
This research project, using the confidential Quarterly Financial Report (QFR) database from the Census Bureau, aims to shed light on the supply-side effects of monetary policy interventions. It will address three key research topics on the misallocation channel of monetary shocks: 1) provide empirical evidence on the sources of capital misallocation; 2) develop a theoretical model incorporating firm size-dependent financial frictions to understand the heterogeneous effects of monetary shocks on firm dynamics related to capital misallocation; and 3) examine the short-term distributional impacts of monetary shocks in relation to capital misallocation.
Project with Matthew Schaffer
This research project focuses on three key areas of international monetary policy and trade dynamics. The first study analyzes the impact of US Federal Reserve policy on US firms' export-import activities using the Longitudinal Foreign Trade Transactions Database (LFTTD). The second study explores how US monetary policy influences global trade flows, with a focus on country-specific impacts. The third project examines the effects of European Central Bank (ECB) policy on trade between the US and euro area countries, highlighting ECB policy spillovers to the US. These studies provide valuable insights into how central bank policies affect international trade.
Inflation Expectations Through the Lens of Artificial Intelligence
Project with Huiyu Li and Tatevik Sekhposyan
This project leverages OpenAI's Large Language Model, ChatGPT-4, to generate real-time forecasts for key economic indicators, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation, Unemployment Rate, Federal Funds Rate, and GDP Growth Rate for the United States, Canada, and globally. By integrating traditional economic data with advanced AI techniques, our research aims to provide a novel perspective on the formation and evolution of inflation expectations and other macroeconomic indicators. An additional experimental approach uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which incorporates top Google search results to provide more context to the forecasts. This integration enhances the model's predictive capabilities by summarizing relevant information from external sources. This innovative approach enables the analysis of large-scale economic data, offering insights that are both timely and relevant for policymakers, financial analysts, and researchers. Through this project, we seek to deepen the understanding of inflation dynamics and contribute to more informed economic decision-making.
Published Papers, R&R, Submitted
- Capital Misallocation: Cyclicality and Sources, March 2020, Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, Vol. 112(C).
- Data Synthesis for Longitudinal Business Data across Three Countries, with Benoit Dostie, Jörg Drechsler, Lars Vilhuber, August 2020, STATISTICS IN TRANSITION new series, 21(3): 223-247
- The Long-Run Effects of Monetary Policy: The Role of R&D Investment in Economic Growth, with Eskander Alvi, August 2024, Economic Modeling,, Vol. 137
- Effect of Monetary Policy on Productivity: Frictions in High-Tech Firms, with Haydory Akbar Ahmed and Khandokar Istiak, North American Journal of Economics and Finance (R&R)
- Spatial Misallocation in Canada, with Herb Emery, Canadian Journal of Regional Science (Forthcoming)
- Price Dispersion and Trade Policy, Review of International Economics (R&R)
- Place-Based Scholarships: Treatment Effects from the Kalamazoo Promise, with W. Jason Beasley, Applied Economics (R&R)
- Applying Machine Learning Methods in Causal Estimation: Analyzing the Benefits of College Athletic Success, with Gerard Tetegan, Journal of Comments and Replications in Economics (Under review)
- The Convenience Yield Channel of Monetary Policy and International Stock Prices, with Matthew Schaffer and Rashed Sardar, Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions & Money (R&R)
- Differences in Firm Growth across Countries: Does it Explain GDP Differences?, Journal of Comparative Economics (Submitted)
- Welfare Effects of the Canada-U.S. Free Trade Agreement: A Product-Level Analysis, Review of World Economics (Submitted)
- Identifying Macro Determinants of Natural Disaster: Applying Machine Learning Approach, with with Pallab Mozumder, Computational Economics (Submitted)
- Estimating the Impacts of the COVID-19 Shock on Household Consumption Patterns, with Nazneen Ahmad, Applied Economics Letters (Submitted)
- Productivity Gains from International Trade in Young and Old Economies, with Maksim Isakin, Macroeconomic Dynamics (Under review)
Work in Progress
- Inflation Expectations Through the Lens of Artificial Intelligence, with Huiyu Li and Tatevik Sekhposyan
- Differential Effects of Monetary Policy on Capital Misallocation, with Pedro Bento and Tatevik Sekhposyan
- Monetary Policy Shocks and Allocative Efficiency across U.S. Firms, with Pedro Bento and Eskander Alvi
- Misallocation and Trade Policy, with Huju Liu
- Dispersion of News Sentiment and Stock Price Return: Applying Deep Learning Approach, with Maksim Isakin
Textbook and Book Chapter
-
Data Science with Generative AI for Economic and Social Issues
- Applies machine learning techniques to causal estimation methods, forecasting, and practical Python exercises for data analysis.
- Learning aids include summaries, exercises, replication codes, LaTeX slides, and Python code access via Google Colab and GitHub.
- Incorporates AI tools like ChatGPT and ChatBot for interactive Q&A, coding assistance, and personalized learning experiences.
- Children in the slums of Dhaka: Diarrhoea Prevalence and its Implications, 2011, Chapter 12 in Environmental Valuation in South Asia, M. N. Murty, Priya Shyamsundar, and Enamul Haque (eds), New York: Cambridge University Press, Vol. 2, PP. 276-305